目錄
- 1、起步
- 項目結構
- App.vue
- webpack.config.js
- 打包構建
- vue-loader 源碼
- template-loader
- 2、模板編譯流程
- parseHTML 階段
- genElement 階段
- compilerToFunction 階段
- parseHTML 階段
- genElement 階段
- 3、總結
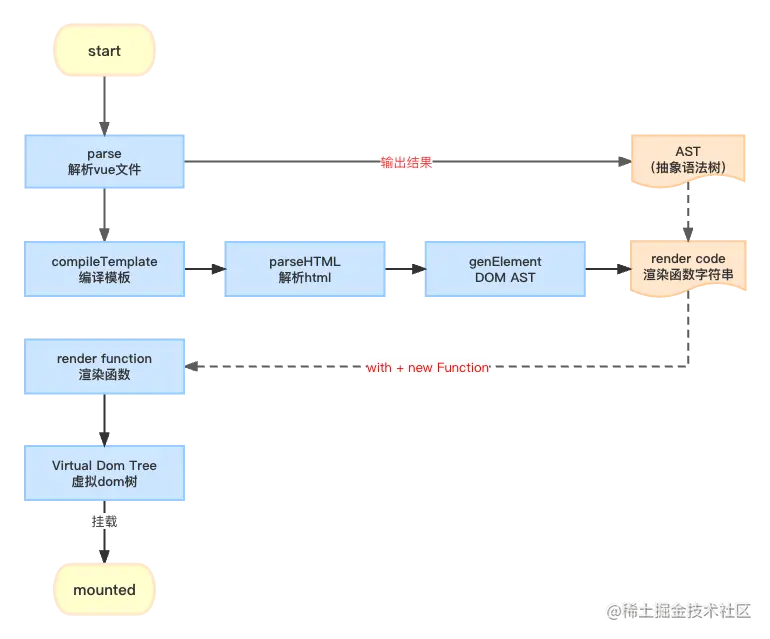
為了更好理解 vue 的模板編譯這里我整理了一份模板編譯的整體流程,如下所示,下面將用源碼解讀的方式來找到模板編譯中的幾個核心步驟,進行詳細說明:
1、起步
這里我使用 webpack 來打包 vue 文件,來分析 vue 在模板編譯中的具體流程,如下所示,下面是搭建的項目結構和文件內容:
項目結構
├─package-lock.json ├─package.json ├─src | ├─App.vue | └index.js ├─dist | └main.js ├─config | ? └webpack.config.js
App.vue
<template>
<div id="box">
? {{ count }}
</div>
</template>
?
<script>
export default {
props: {},
data() {
? return {
? ? count: 0
? }
}
}
</script>
?
<style scoped>
#box {
background: red;
}
</style>
webpack.config.js
const { VueLoaderPlugin } = require('vue-loader')
?
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
module: {
? rules: [
? ? {
? ? ? test: /.vue$/,
? ? ? loader: 'vue-loader'
? ? },
? ? // 它會應用到普通的 `.js` 文件
? ? // 以及 `.vue` 文件中的 `<script>` 塊
? ? {
? ? ? test: /.js$/,
? ? ? loader: 'babel-loader'
? ? },
? ? // 它會應用到普通的 `.css` 文件
? ? // 以及 `.vue` 文件中的 `<style>` 塊
? ? {
? ? ? test: /.css$/,
? ? ? use: [
? ? ? ? 'vue-style-loader',
? ? ? ? 'css-loader'
? ? ? ]
? ? }
? ]
},
plugins: [
? new VueLoaderPlugin()
]
}
如上 webpack.config.js 所示,webpack 可以通過 vue-loader 識別 vue 文件,vue-loader 是 webpack 用來解析 .vue 文件的 loader,主要作用是將單文件組件(SFC),解析成為 webpack 可識別的 JavaScript 模塊。
打包構建
搭建好整個目錄項目后,執行 npm run build ,會將 vue 文件解析打包成對應的 bundle,并輸出至 dist 目錄下,下面是打包后的產出,對應 App.vue 的產物:
/***/ "./src/App.vue"
?
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/* harmony export */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, {
/* harmony export */ ? "default": () => (__WEBPACK_DEFAULT_EXPORT__) \n/* harmony export */
});
?
var _App_vue_vue_type_template_id_7ba5bd90_scoped_true___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__("./src/App.vue?vue&type=template&id=7ba5bd90&scoped=true&");
?
var _App_vue_vue_type_script_lang_js___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__ = __webpack_require__( "./src/App.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&");
?
?
?
var _node_modules_vue_loader_lib_runtime_componentNormalizer_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__ = __webpack_require__("./node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js");
?
var component = (0, _node_modules_vue_loader_lib_runtime_componentNormalizer_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__["default"])(
_App_vue_vue_type_script_lang_js___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__["default"],
_App_vue_vue_type_template_id_7ba5bd90_scoped_true___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.render, _App_vue_vue_type_template_id_7ba5bd90_scoped_true___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.staticRenderFns, false, null, "7ba5bd90", null,/* hot reload */
)
從上方的產物可以看出,App.vue 文件被編譯分為三塊,_App_vue_vue_type_template_id_7ba5bd90_scoped_true___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ 、 _App_vue_vue_type_script_lang_js___WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__,_node_modules_vue_loader_lib_runtime_componentNormalizer_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_2__,這三個模塊恰好對應vue模板中的 template、script、style這三個標簽的模板內容,所以得出結論:vue-loader 會將 vue 模板中的template、script、style 標簽內容分解為三個模塊。 為此,我找到 vue-loader 的源碼,下面分析其源碼邏輯:
vue-loader 源碼
源碼里很清楚的可以看到 vue-loader 使用了 vue/compiler-sfc 中的 parse 方法對 vue 的源文件進行的解析,將模板語法解析為一段可描述的對象
module.exports = function (source) {
// 這里就是.vue文件的AST
const loaderContext = this
?
? ...
// 解析.vue原文件,source對應的就是.vue模板
const descriptor = compiler.parse({
? source,
? compiler: options.compiler || templateCompiler,
? filename,
? sourceRoot,
? needMap: sourceMap
})
?
? ...
?
// 使用webpack query source
let templateImport = `var render, staticRenderFns`
let templateRequest
if (descriptor.template) {
? const src = descriptor.template.src || resourcePath
? const idQuery = `&id=${id}`
? const scopedQuery = hasScoped ? `&scoped=true` : ``
? const attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(descriptor.template.attrs)
? // const tsQuery =
? // options.enableTsInTemplate !== false && isTS ? `&ts=true` : ``
? const query = `?vue&type=template${idQuery}${scopedQuery}${attrsQuery}${inheritQuery}`
? const request = (templateRequest = stringifyRequest(src + query))
? templateImport = `import { render, staticRenderFns } from ${request}`
}
?
? ...
?
code += `\nexport default component.exports`
return code
}
對 descriptor 進行打印,輸出結果如下,vue-loader 對源文件編譯后,vue 模板會被轉化成抽象語法樹(AST),此處便是模板編譯的入口,使用編譯后的 AST 將 vue 模板拆分為 template 、script 和 style 三部分,方便后面 webpack 通過 resourceQuery 匹配分發到各個loader 進行二次解析編譯,template 部分會被 template-loader 進行二次編譯解析,最終生成render 函數。
{
source: '<template>\n' +
? ' <div id="box">\n' +
? ' ? {{ count }}\n' +
? ' </div>\n' +
? '</template>\n' +
? '\n' +
? '<script>\n' +
? 'export default {\n' +
? ' props: {},\n' +
? ' data() {\n' +
? ' ? return {\n' +
? ' ? ? count: 0\n' +
? ' ? }\n' +
? ' }\n' +
? '}\n' +
? '</script>\n' +
? '\n' +
? '<style>\n' +
? '#box {\n' +
? ' background: red;\n' +
? '}\n' +
? '</style>\n',
filename: 'App.vue',
template: {
? type: 'template',
? content: '\n<div id="box">\n {{ count }}\n</div>\n',
? start: 10,
? end: 53,
? attrs: {}
},
script: {
? type: 'script',
? content: '\n' +
? ? 'export default {\n' +
? ? ' props: {},\n' +
? ? ' data() {\n' +
? ? ' ? return {\n' +
? ? ' ? ? count: 0\n' +
? ? ' ? }\n' +
? ? ' }\n' +
? ? '}\n',
? start: 74,
? end: 156,
? attrs: {}
},
....
}
template-loader
template-loader 的作用是將 import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./App.vue?vue&type=template&id=7ba5bd90&" 模塊編譯成 render 函數并導出,以下是編譯產物:
// 編譯前
<div id="box">
{{ count }}
</div>
?
// 編譯后
var render = function render() {
var _vm = this,
? _c = _vm._self._c
return _c("div", { attrs: { id: "box" } }, [
? _vm._v("\n " + _vm._s(_vm.count) + "\n"),
])
}
var staticRenderFns = []
render._withStripped = true
?
export { render, staticRenderFns }
template-loader?核心原理是通過?vue/compiler-sfc?將模板轉換成為 render 函數,并返回 template 編譯產物
module.exports = function (source) {
const loaderContext = this
? ...
// 接收模板編譯核心庫
const { compiler, templateCompiler } = resolveCompiler(ctx, loaderContext)
?
? ...
?
// 開啟編譯
const compiled = compiler.compileTemplate(finalOptions)
?
? ...
?
// 編譯后產出,code就是render函數
const { code } = compiled
?
// 導出template模塊
return code + `\nexport { render, staticRenderFns }`
}
2、模板編譯流程
vue/compiler-sfc 是模板編譯的核心庫,在 vue2.7 版本中使用,而 vue2.7 以下的版本都是使用vue-template-compiler,本質兩個包的功能是一樣的,都可以將模板語法編譯為 JavaScript,接下來我們來解析一下在模板編譯過程中使用的方法:
parseHTML 階段
可以將 vue 文件中的模板語法轉義為 AST,為后續創建 dom 結構做預處理
export function parseHTML(html, options: HTMLParserOptions) {
// 存儲解析后的標簽
const stack: any[] = []
const expectHTML = options.expectHTML
const isUnaryTag = options.isUnaryTag || no
const canBeLeftOpenTag = options.canBeLeftOpenTag || no
let index = 0
let last, lastTag
// 循環 html 字符串結構
while (html) {
// 記錄當前最新html
last = html
if (!lastTag || !isPlainTextElement(lastTag)) {
// 獲取以 < 為開始的位置
let textEnd = html.indexOf('<')
if (textEnd === 0) {
// 解析注釋
if (comment.test(html)) {
const commentEnd = html.indexOf('-->')
if (commentEnd >= 0) {
if (options.shouldKeepComment && options.comment) {
options.comment(
html.substring(4, commentEnd),
index,
index + commentEnd + 3
)
}
advance(commentEnd + 3)
continue
}
}
// 解析條件注釋
if (conditionalComment.test(html)) {
const conditionalEnd = html.indexOf(']>')
if (conditionalEnd >= 0) {
advance(conditionalEnd + 2)
continue
}
}
// 解析 Doctype
const doctypeMatch = html.match(doctype)
if (doctypeMatch) {
advance(doctypeMatch[0].length)
continue
}
// 解析截取結束標簽
const endTagMatch = html.match(endTag)
if (endTagMatch) {
const curIndex = index
advance(endTagMatch[0].length)
parseEndTag(endTagMatch[1], curIndex, index)
continue
}
// 解析截取開始標簽
const startTagMatch = parseStartTag()
if (startTagMatch) {
handleStartTag(startTagMatch)
if (shouldIgnoreFirstNewline(startTagMatch.tagName, html)) {
advance(1)
}
continue
}
}
let text, rest, next
if (textEnd >= 0) {
rest = html.slice(textEnd)
while (
!endTag.test(rest) &&
!startTagOpen.test(rest) &&
!comment.test(rest) &&
!conditionalComment.test(rest)
) {
// < in plain text, be forgiving and treat it as text
next = rest.indexOf('<', 1)
if (next < 0) break
textEnd += next
rest = html.slice(textEnd)
}
text = html.substring(0, textEnd)
}
// 純文本節點
if (textEnd < 0) {
text = html
}
// 截取文本節點
if (text) {
advance(text.length)
}
if (options.chars && text) {
options.chars(text, index - text.length, index)
}
} else {
let endTagLength = 0
const stackedTag = lastTag.toLowerCase()
const reStackedTag =
reCache[stackedTag] ||
(reCache[stackedTag] = new RegExp(
'([\s\S]*?)(</' + stackedTag + '[^>]*>)',
'i'
))
const rest = html.replace(reStackedTag, function (all, text, endTag) {
endTagLength = endTag.length
if (!isPlainTextElement(stackedTag) && stackedTag !== 'noscript') {
text = text
.replace(/<!--([\s\S]*?)-->/g, '$1') // #7298
.replace(/<![CDATA[([\s\S]*?)]]>/g, '$1')
}
if (shouldIgnoreFirstNewline(stackedTag, text)) {
text = text.slice(1)
}
if (options.chars) {
options.chars(text)
}
return ''
})
index += html.length - rest.length
html = rest
parseEndTag(stackedTag, index - endTagLength, index)
}
if (html === last) {
options.chars && options.chars(html)
break
}
}
// 清空閉合標簽
parseEndTag()
// 截取標簽,前后推進位置
function advance(n) {
index += n
html = html.substring(n)
}
// 解析開始標簽
function parseStartTag() {
const start = html.match(startTagOpen)
if (start) {
const match: any = {
tagName: start[1],
attrs: [],
start: index
}
advance(start[0].length)
let end, attr
while (
!(end = html.match(startTagClose)) &&
(attr = html.match(dynamicArgAttribute) || html.match(attribute))
) {
attr.start = index
advance(attr[0].length)
attr.end = index
match.attrs.push(attr)
}
if (end) {
match.unarySlash = end[1]
advance(end[0].length)
match.end = index
return match
}
}
}
// 匹配處理開始標簽
function handleStartTag(match) {
const tagName = match.tagName
const unarySlash = match.unarySlash
if (expectHTML) {
if (lastTag === 'p' && isNonPhrasingTag(tagName)) {
parseEndTag(lastTag)
}
if (canBeLeftOpenTag(tagName) && lastTag === tagName) {
parseEndTag(tagName)
}
}
const unary = isUnaryTag(tagName) || !!unarySlash
const l = match.attrs.length
const attrs: ASTAttr[] = new Array(l)
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
const args = match.attrs[i]
const value = args[3] || args[4] || args[5] || ''
const shouldDecodeNewlines =
tagName === 'a' && args[1] === 'href'
? options.shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref
: options.shouldDecodeNewlines
attrs[i] = {
name: args[1],
value: decodeAttr(value, shouldDecodeNewlines)
}
if (__DEV__ && options.outputSourceRange) {
attrs[i].start = args.start + args[0].match(/^\s*/).length
attrs[i].end = args.end
}
}
if (!unary) {
stack.push({
tag: tagName,
lowerCasedTag: tagName.toLowerCase(),
attrs: attrs,
start: match.start,
end: match.end
})
lastTag = tagName
}
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, attrs, unary, match.start, match.end)
}
}
// 解析結束標簽
function parseEndTag(tagName?: any, start?: any, end?: any) {
let pos, lowerCasedTagName
if (start == null) start = index
if (end == null) end = index
// Find the closest opened tag of the same type
if (tagName) {
lowerCasedTagName = tagName.toLowerCase()
for (pos = stack.length - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) {
if (stack[pos].lowerCasedTag === lowerCasedTagName) {
break
}
}
} else {
// If no tag name is provided, clean shop
pos = 0
}
if (pos >= 0) {
// Close all the open elements, up the stack
for (let i = stack.length - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
if (__DEV__ && (i > pos || !tagName) && options.warn) {
options.warn(`tag <${stack[i].tag}> has no matching end tag.`, {
start: stack[i].start,
end: stack[i].end
})
}
if (options.end) {
options.end(stack[i].tag, start, end)
}
}
// Remove the open elements from the stack
stack.length = pos
lastTag = pos && stack[pos - 1].tag
} else if (lowerCasedTagName === 'br') {
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, [], true, start, end)
}
} else if (lowerCasedTagName === 'p') {
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, [], false, start, end)
}
if (options.end) {
options.end(tagName, start, end)
}
}
}
}
genElement 階段
genElement?會將?AST?預發轉義為字符串代碼,后續可將其包裝成 render 函數的返回值
// 將AST預發轉義成render函數字符串
export function genElement(el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {
if (el.parent) {
el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre
}
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
// 輸出靜態樹
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
// 處理v-once指令
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
// 處理循環結構
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
// 處理條件語法
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
// 處理子標簽
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
// 處理插槽
return genSlot(el, state)
} else {
// 處理組件和dom元素
...
return code
}
}
通過genElement函數包裝處理后,將vue?模板的?template?標簽部分轉換為?render?函數,如下所示:
const compiled = compiler.compileTemplate({
source: '\n' +
'<div id="box">\n' +
' {{ count }}\n' +
' <button @add="handleAdd">+</button>\n' +
'</div>\n'
});
const { code } = compiled;
// 編譯后
var render = function render() {
var _vm = this,
_c = _vm._self._c
return _c("div", { attrs: { id: "box" } }, [
_vm._v("\n " + _vm._s(_vm.count) + "\n "),
_c("button", { on: { add: _vm.handleAdd } }, [_vm._v("+")]),
])
}
var staticRenderFns = []
render._withStripped = true
compilerToFunction 階段
將?genElement?階段編譯的字符串產物,通過?new Function將 code 轉為函數
export function createCompileToFunctionFn(compile: Function): Function {
const cache = Object.create(null)
return function compileToFunctions(
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions,
vm?: Component
): CompiledFunctionResult {
...
// 編譯
const compiled = compile(template, options)
// 將genElement階段的產物轉化為function
function createFunction(code, errors) {
try {
return new Function(code)
} catch (err: any) {
errors.push({ err, code })
return noop
}
}
const res: any = {}
const fnGenErrors: any[] = []
// 將code轉化為function
res.render = createFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors)
res.staticRenderFns = compiled.staticRenderFns.map(code => {
return createFunction(code, fnGenErrors)
})
...
}
}
為了方便理解,使用斷點調試,來看一下 compileTemplate 都經歷了哪些操作:

首先會判斷是否需要預處理,如果需要預處理,則會對 template 模板進行預處理并返回處理結果,此處跳過預處理,直接進入?actuallCompile?函數
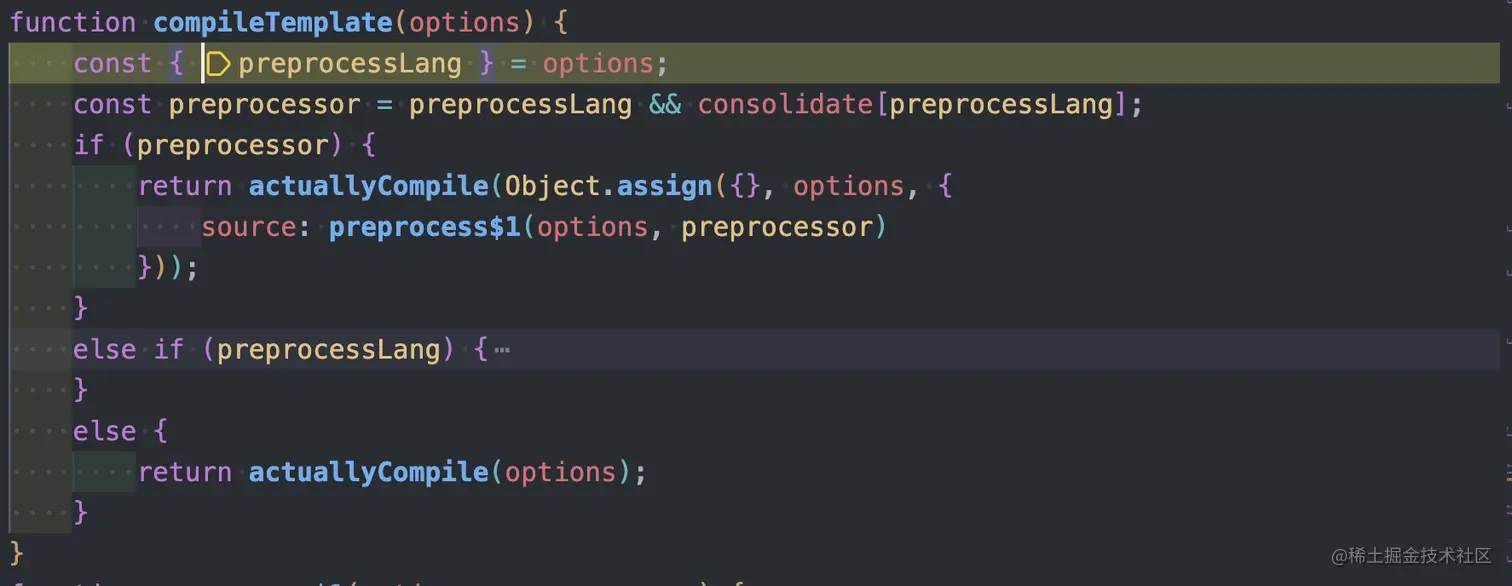
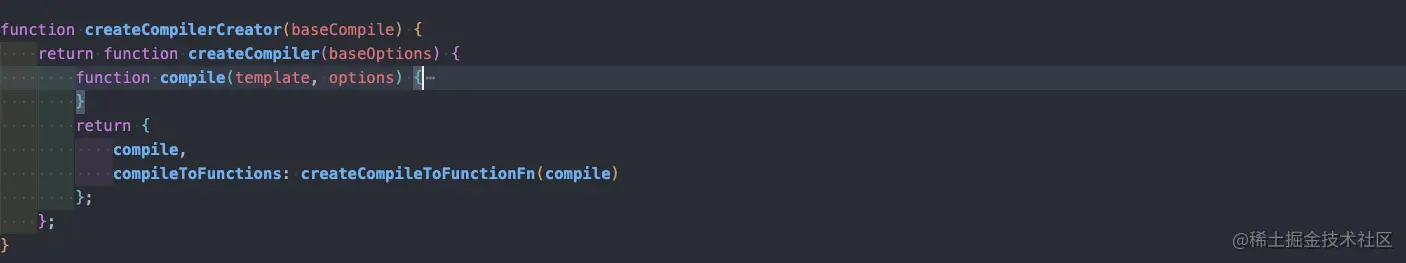
這里可以看到本身內部還有一層編譯函數對 template 進行編譯,這才是最核心的編譯方法,而這個 compile 方法來源于?createCompilerCreator
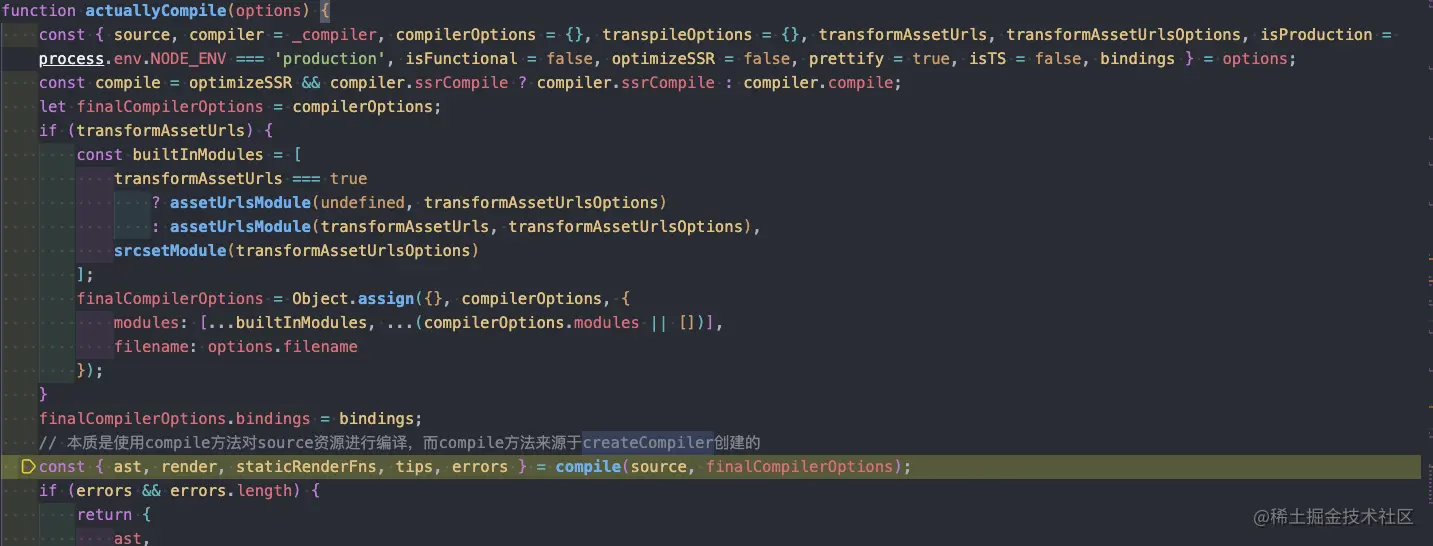
createCompilerCreator 返回了兩層函數,最終返回值則是 compile 和 compileToFunction,這兩個是將 template 轉為 render 函數的關鍵,可以看到 template 會被解析成 AST 樹,最后通過 generate 方法轉義成函數 code,接下來我們看一下parse函數中是如何將 template 轉為 AST 的。
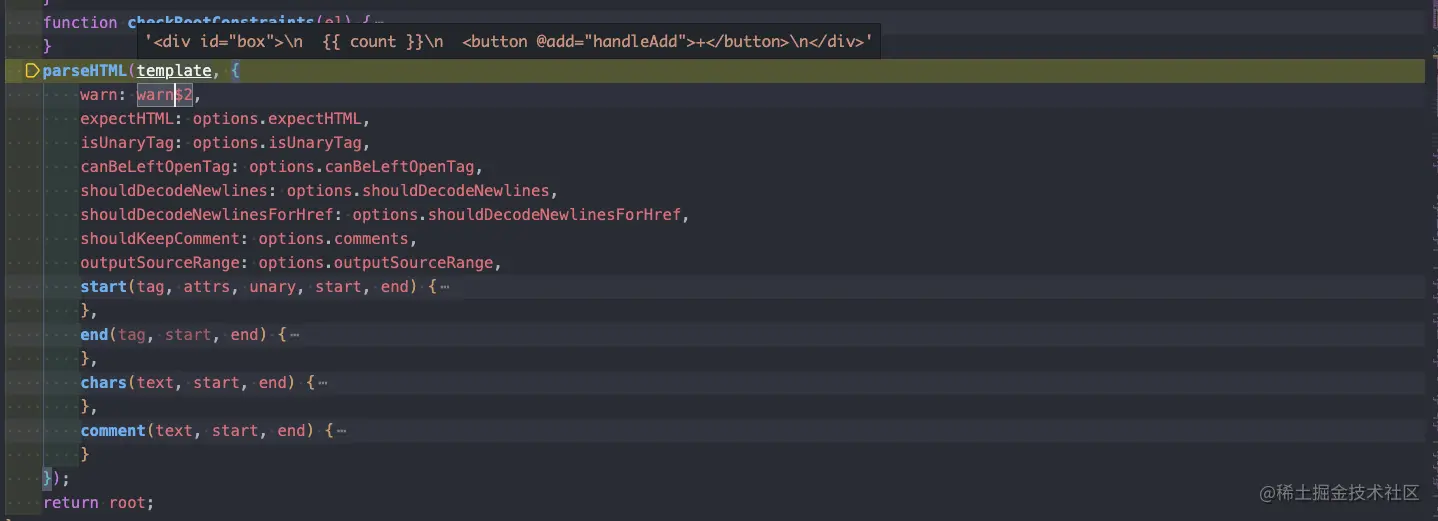
繼續向下 debug 后,會走到 parseHTML 函數,這個函數是模板編譯中用來解析 HTML 結構的核心方法,通過回調 + 遞歸最終遍歷整個 HTML 結構并將其轉化為 AST 樹。
parseHTML 階段
使用 parseHTML 解析成的 AST 創建 render 函數和 Vdom
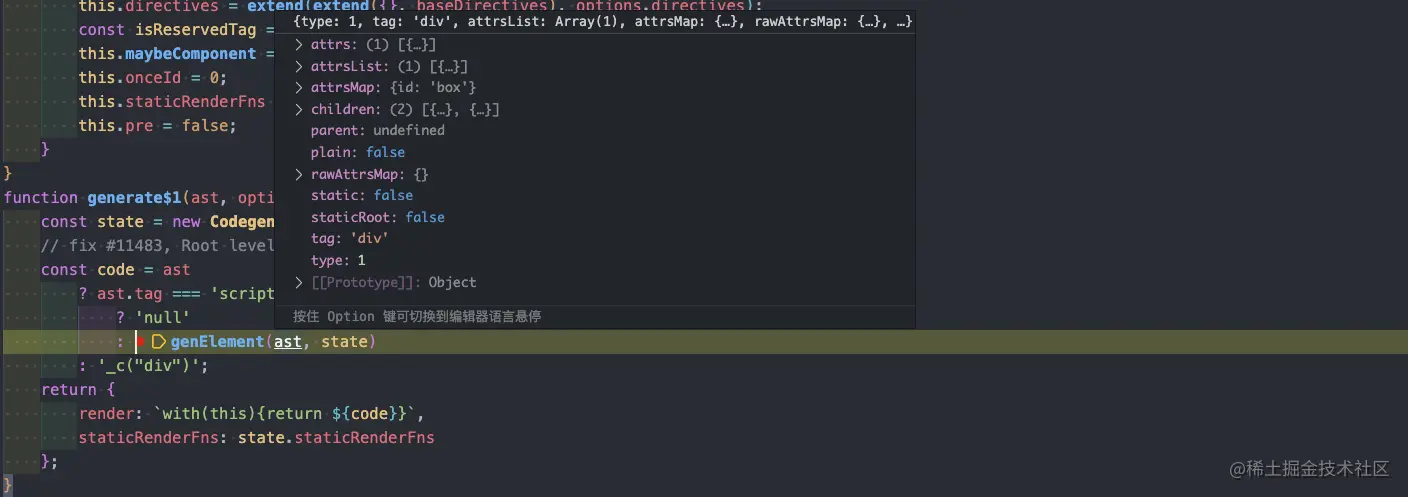
genElement 階段
將 AST 結構解析成為虛擬 dom 樹
最終編譯輸出為 render 函數,得到最終打包構建的產物。

3、總結
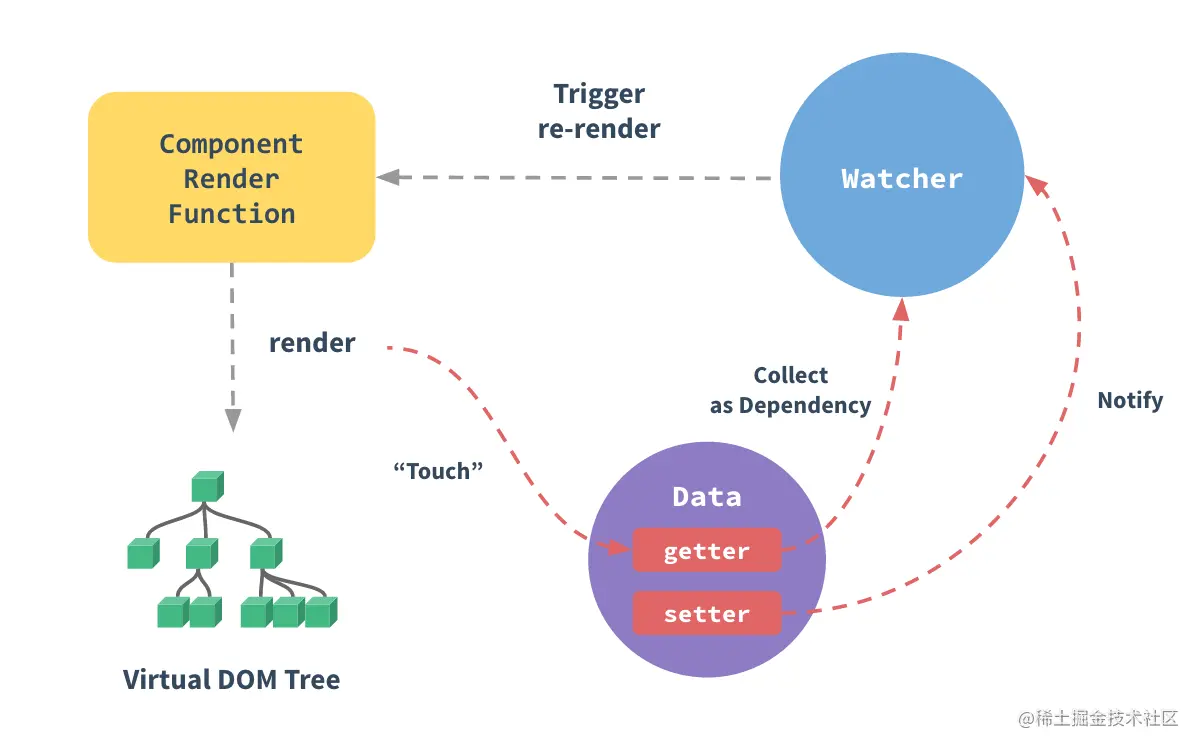
到此我們應該了解了 vue 是如何打包構建將模板編譯為渲染函數的,有了渲染函數后,只需要將渲染函數的 this 指向組件實例,即可和組件的響應式數據綁定。vue 的每一個組件都會對應一個渲染 Watcher ,他的本質作用是把響應式數據作為依賴收集,當響應式數據發生變化時,會觸發 setter 執行響應式依賴通知渲染 Watcher 重新執行 render 函數做到頁面數據的更新。
以上就是Vue2模版編譯流程詳解的詳細內容,更多關于Vue2模版編譯的資料請關注技圈網其它相關文章!